top of page
PINGS-X: Gaussian Splatting for Super-Resolution of 4D Flow MRI
Center for Precision Medicine Platform Based on Smart Hemo-Dynamic Index
The Multiscale Heat & Fluid Flow Lab (MFL), in collaboration with the Spatial AI Lab (SAIL), utilizes 4D flow MRI—a non-invasive modality that captures time-resolved blood flow velocity fields—to investigate complex hemodynamics. However, its clinical use is limited by long scan times and low spatial resolution. To address this, the team developed PINGS-X (Physics-Informed Normalized Gaussian Splatting with Axes Alignment), a novel super-resolution framework inspired by 3D Gaussian splatting in computer vision. PINGS-X represents flow using spatially aligned Gaussians, each encoding local velocity and pressure, and predicts values via normalized Gaussian-weighted summation. Gaussian splatting enables high computational efficiency, adaptive resolution, and fast convergence. Crucially, PINGS-X incorporates physical laws—continuity and Navier-Stokes equations—into its loss function, ensuring physically consistent reconstructions. Applied to synthetic and real 4D flow MRI data, PINGS-X achieves high-fidelity super-resolution, recovering fine-scale flow structures and reducing velocity error by over 50% compared to baseline methods, while significantly reducing training time.
Artificial
Intelligence
Human
Healthcare

Research Center & Sponsor
1.
2.
3.
4.
Center for Precision Medicine Platform Based on Smart Hemo-Dynamic Index Research
National Research Foundation
Engineering Research Center
Spatial AI Lab.
Super-Resolution 4D Flow MRI data with Physics-Informed Neural Operator
Center for Precision Medicine Platform Based on Smart Hemo-Dynamic Index
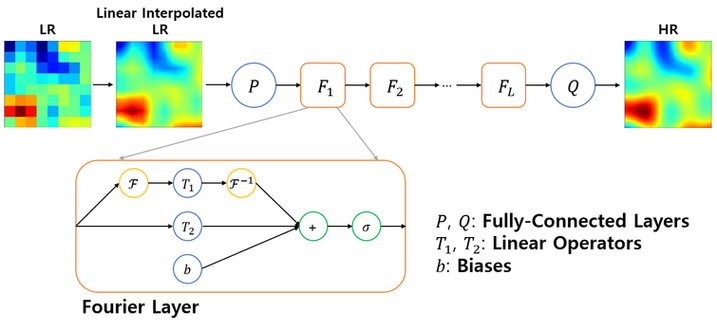
The Multiscale Heat & Fluid Flow Lab(MFL) utilizes 4D flow MRI to investigate complex flow phenomena in biological and engineering systems. Although 4D Flow MRI can accurately measure three-dimensional flow fields, it has limitations in acquiring high spatial resolution data. To overcome this limitation, MFL developed a Super-Resolution Physics-Informed Neural Operator(SRPINO). High-resolution flow field data were down sampled to create low-resolution data, which were then used to train a model based on the Fourier Neural Operator (FNO) architecture. The model takes low-resolution input and outputs high-resolution flow field predictions. To ensure that the predicted high-resolution flow fields satisfy the conservation of mass, the model was trained with an additional constraint based on the continuity equation. Furthermore, to address FNO’s limitations with non-periodic data—due to its affinity for periodic functions—padding and Fourier continuation techniques were employed, enabling the model to generalize to more typical, non-periodic flow fields. Validation with randomly generated flow field data demonstrated that SRPINO can predict high-resolution outputs within few seconds.
Artificial
Intelligence
Human
Healthcare
Research Center & Sponsor
1.
2.
3.
Center for Precision Medicine Platform Based on Smart Hemo-Dynamic Index Research
National Research Foundation
Engineering Research Center
Estimation Aorta Pressure Distribution Using Physics-Informed Neural Network
Center for Precision Medicine Platform Based on Smart Hemo-Dynamic Index
Pressure and wall shear stress constitute the dominant hemodynamic loads on the vascular endothelium but mapping the three‑dimensional intravascular pressure distribution remains difficult: direct measurement is invasive, and high‑fidelity CFD reconstructions, though reliable, demand hours to days of computational time. Physics‑informed neural networks (PINNs) offer a compelling alternative by embedding the Navier–Stokes equations into a deep‑learning framework, enabling near‑real‑time pressure predictions that are robust to noisy or sparse data, free from meshing overhead, and able to accommodate complex or patient‑specific boundary conditions. Leveraging these advantages, the Multiscale Heat & Fluid Flow Laboratory (MFL) is developing a PINN‑based model that ingests velocity measurements and instantly delivers spatially resolved pressure fields for patient‑specific vascular geometries, accelerating both research and clinical decision‑making
Artificial
Intelligence
Human
Healthcare

Research Center & Sponsor
1.
2.
3.
Center for Precision Medicine Platform Based on Smart Hemo-Dynamic Index Research
National Research Foundation
Engineering Research Center
AI Model Capable of Predicting Design Factors That Influence Flow Patterns
Flow Noise Research Center
The Multiscale Heat & Fluid Flow Lab (MFL) developed an AI model to evaluate the influence of changes in design factors affecting aerodynamics by using wake flow. The accurate assessment of how design changes influence aerodynamic performance is a critical challenge in the automotive design process. However, results of the traditional assessment vary depending on the experience of the evaluators performing this process when multiple designs change simultaneously. Specifically, MFL trained ResNet18 model with wake flow and its corresponding design factors using two different approaches – one is Multi-label Classification to identify whether design elements changed, enhancing interpretability through grad-CAM visualization and the other is Multi-target Regression model to quantitatively measure the extent of design element changes. As a result, both models effectively analyzed design elements and could comprehend their impact on aerodynamics. This research is being conducted in collaboration with HYUNDAI NGV.
Artificial
Intelligence
Future
Mobility

Research Presentation Video
1.
2.
3.
J. Kim, S. Song, I. Jang, J. Hong, C. Yun, "Development Of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Model Analyzing The Wake Flow To Improve Vehicle Aerodynamic Performance", KSVI, 2023, April. 20, Seoul, Korea
J. Kim, C. Yun, I. Jang, J. Hong, S. Song, "Machine Learning for Identifying Design Changes of Vehicle with Wake Flow", FSSIC, 2023, August. 31, Busan, Korea
J. Kim, I. Jang, S. Song, "Analyzing The Relationship Between Wake Flow Patterns and Design Element Changes of Vehicles Using Machine Learning", APS DFD, 2023, November. 20, Washington DC, USA
Flow Noise Research Center
HYUNDAI NGV
Research Center & Sponsor
1.
2.

bottom of page